How do businesses make timely decisions with efficiency? One approach uses streaming (real-time) data applications that collect, analyze, and offer insights about data as it is generated, as opposed to systems that store data and process it later – even if stored for mere minutes. Data’s role in decision-making for organizations depends on how recently it is received, processed, and analyzed to inform our decisions.
Data comes in from many locales—on-premises, in the cloud, at the edge, etc.—and is then digested and stored before being incorporated into applications. Often described as “data at rest,” this storage renders data static on a drive or in a database. While this is acceptable for many processes, when garnering insights for real-time purposes or decision-making, data at rest creates limitations that impact how to interpret insights and make decisions.
Continuous Creation and Dissemination of Data in Motion
Over 80% of all Fortune 100 companies rely on streaming data technologies like Apache Kafka. Streaming data is continuously created and disseminated, typically traveling in smaller bundles or streams obtained and handled by downstream system apparatuses in real-time. This data holds the highest value in processes requiring contemporaneous insights that provide essential details to support decision-making efforts. For example, fraud detection efforts are well suited to apply real-time data to analysis, allowing for immediate insights far exceeding batch-processed data and keeping their data current.
Organizations often find challenges in extracting the most from their streaming data. Common concerns include:
- The analysis of data stored for any period as it fails to be true real-time analysis.
- The expense of processing various data streams at once.
- The complexity and drain on resources of simultaneously processing and managing numerous open-source data systems, vendors, and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- The impact and compounding of latency preventing true real-time insights.
These concerns influence organizations when selecting the best data applications for their business.
Use Cases Illustrating the Need for Data In Motion
Many industries benefit from real-time streaming data insights – from retailers looking to track inventory to transportation companies trying to reduce fuel costs to financial institutions providing personalized experiences or recommendations.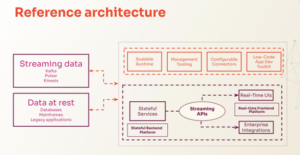
Favored use cases include:
- Real-time customer 360: Unlock an accurate real-time picture of what a customer is experiencing in the real world to drive personalized offers and recommendations.
- Anomaly detection: Quickly identify data anomalies that indicate more significant issues, such as transaction fraud, IoT malfunction or shutdown, adverse external events, etc., and automate mitigation efforts before irreparable damage is done.
- Inventory management and tracking: Gain real-time insight into inventory status and streamline supply chain processes for optimal resource allocation.
Customer Impact of Real-Time Streaming Data
End-users lost almost $8.8 billion in 2022 because of fraud — more than 30% from the previous year. By implementing streaming data applications that meet compliance requirements, using data from warehouse sources to learn patterns and better detect future malicious behavior, and integrating streaming data applications with other technologies, organizations can potentially reduce their losses and better prevent fraud in the future.
Additionally, real-time streaming data applications can amplify productivity and improve the customer experience, which can maximize return on investment (ROI). Customer-facing applications are also positively impacted by real-time data. Utilizing real-time streaming data can increase customer engagement and improve customer satisfaction.
What if developers could build streaming data applications in minutes versus months? Imagine the operational cost savings and the rapid deployment of technology that improves the customer experience and dramatically improves an organization’s bottom line.
Benefits of Building Streaming Data Applications Quickly
Technology advances now provide developers with open source full-stack streaming data application development platforms – enterprises can continuously perform stream-to-stream joins at scale and isolate events at a real-world object level.
Platforms that integrate with popular streaming data technologies (Apache Kafka, AWS Kinesis, Apache Pulsar, etc.) allow business decision-makers to gain a real-time view into their business for better informed and automated decisions at network-level latency. Streaming data applications have broad applicability across industries.
Today’s platforms deliver streaming data application performance and outcomes at unprecedented scale and high efficiency. Companies such as Verizon, Itron, Cubic, Rockwell Automation, RTA, ARM, and Juniper Networks are realizing benefits like:
| Scale | 100M+ stateful entities | 1B+ multiplexed streams | 200M+ changes per second | Sub-second, full-stack latency |
| Efficiency | 10x faster time-to-value | 4x fewer engineering hours | 5x less middleware | 70% lower total cost of ownership |
10x faster time to value: A fully integrated platform saves organizations months designing, building, and testing traditional architectures with multiple complex open-source data systems, application servers, and UI frameworks.
It is possible to build streaming data applications without the need for:
- Stream processing frameworks (Pinot, Presto)
- Additional databases (Druid, Clickhouse, MongoDB)
- Additional applications servers (Spring, NodeJS, .Net)
- UI frameworks (Angular, React)
More than 70% lower TCO: Organizations can eliminate the complexity in building and maintaining phases for streaming data applications with a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over 70% lower than a traditional architecture. The cost savings come from:
- Lower infrastructure spend: Reductions in infrastructure bills by 80% by scaling the architecture on fewer data systems and far fewer nodes/servers.
- Performing stream-to-stream joins at scale: Instead of executing an additional query every time new information needs to join to a real-world object, the solutions isolate events and streams at a real-world object level—customers, assets, shipping trucks, IoT devices, etc. Keeping the data in motion throughout the application stack at network-level latency is now possible.
- Not hiring SMEs and paying multiple software vendors: Using various open-source data systems requires hiring SMEs for each open-source data system AND subscribing to different software vendors to build streaming applications with inherent latencies. All of which are expensive. Full-stack streaming data application platforms allow organizations to rely on just one software vendor.
- 4x fewer engineering hours: With one integrated system and 5x fewer connections to maintain, it is now possible to free up a significant number of engineering hours that would have otherwise gone into designing, building, testing, connecting, upgrading, and maintaining complex open-source data systems.
The three core technological innovations that make these solutions possible:
- Stateful services ensure that streaming data applications have all the data and context they need to act when a new message arrives.
- Streaming APIs ensure that you can stream incremental updates to API clients and observe real‑time outputs of business logic without polling for changes.
- Real-time user interfaces (UIs) guarantee that users always have a live view of their operations, as broad or as granular as needed, to understand and immediately respond to real-world events.
Before you get started with this approach of having an integrated full-stack streaming data application development platform proven at scale with various enterprises to achieve the benefits of 10x faster time to value and reducing TCO by over 70%, it is important to learn more about these technological innovations and the benefits they may offer your organization.
About the author: Aditya Chidurala is the director of product marketing for Nstream, which he recently joined after four years at Confluent. Aditya has a deep understanding of the open-source streaming data software ecosystem and has worked for over a decade in B2B marketing. He is responsible for developing the positioning, messaging, and industry vertical and horizontal use cases enabled by the Nstream Platform. He holds a bachelor’s degree in electrical engineering from IIT Roorkee and an MBA from USC Marshall School of Business. You can see his LinkedIn profile here.
Nstream, which he recently joined after four years at Confluent. Aditya has a deep understanding of the open-source streaming data software ecosystem and has worked for over a decade in B2B marketing. He is responsible for developing the positioning, messaging, and industry vertical and horizontal use cases enabled by the Nstream Platform. He holds a bachelor’s degree in electrical engineering from IIT Roorkee and an MBA from USC Marshall School of Business. You can see his LinkedIn profile here.
Related Items:
Yes, Real-Time Streaming Data Is Still Growing
Open Source Provides Path to Real-Time Stream Processing
Merging Batch and Stream Processing in a Post Lambda World
The post Using Streaming Data Applications to Power Decision-Making appeared first on Datanami.



0 Commentaires